|
ABOUT THE DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO With a population of around 111 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous nominally Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo; Central African Republic; South Sudan; Uganda; Rwanda; Burundi; Tanzania (across Lake Tanganyika); Zambia; Angola; the Cabinda exclave of Angola; and the South Atlantic Ocean. The official language, since the colonial period, is French, one of the languages of Belgium. Four other languages, all of them Bantu-based, have the status of national language: Kikongo-Kituba, Lingala, Swahili, and Tshiluba. The oil sector accounts for about half of the country's gross domestic product (GDP) and 80% of its exports, making it the third largest producer in Sub-Saharan Africa. However, the main source of income is its mineral deposits. The main cash crops include coffee, palm oil, rubber, cotton, sugar, tea and cocoa. Food crops also include cassava, plantains, maize, groundnuts, and rice.
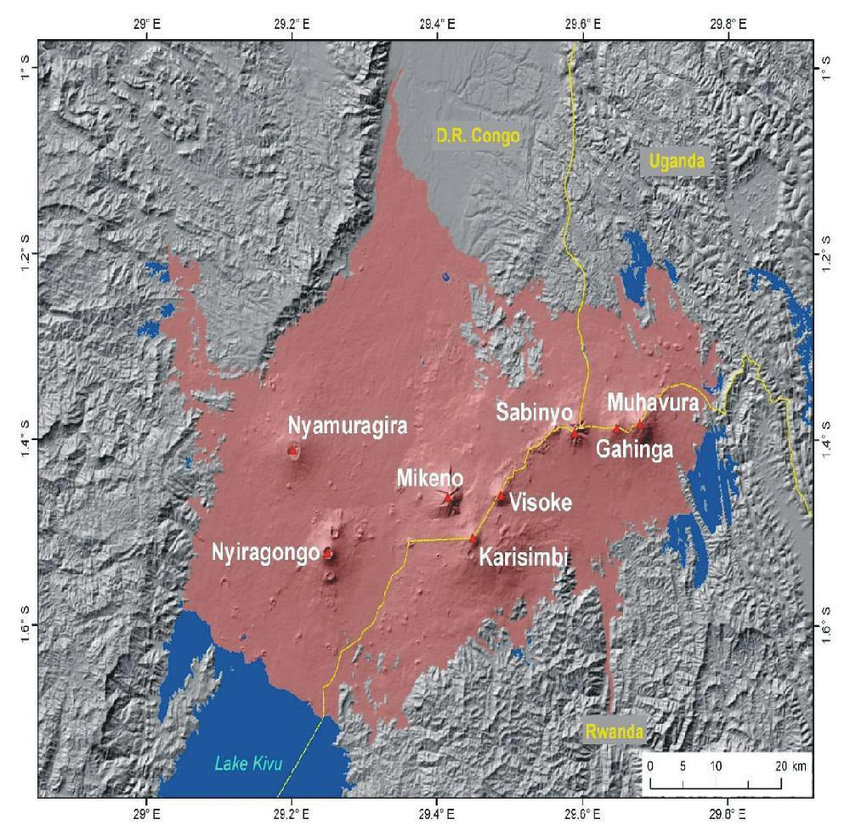
Its rainforests harbor many rare and endemic species, such as the chimpanzee and the bonobo. It is home to more than 10,000 types of plants, 600 timber species, as well as 1,000 bird species, 280 reptile species, and 400 mammal species, including the forest elephant, gorilla, forest buffalo, bongo, and okapi. Many of these wildlife species are threatened animals such as large lowland gorillas and chimpanzees. However, the decades-long conflict over minerals is where the mountain gorilla has had its habitat. They live in two isolated groups – one in the Virunga volcanoes – spanning the borders of Rwanda, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and one in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park in Uganda, contiguous with DRC's Sarambwe Nature Reserve. These mountain gorillas are second on the WWF list of most endangered animals. On this page, you can see the species living in North Kivu. |
|
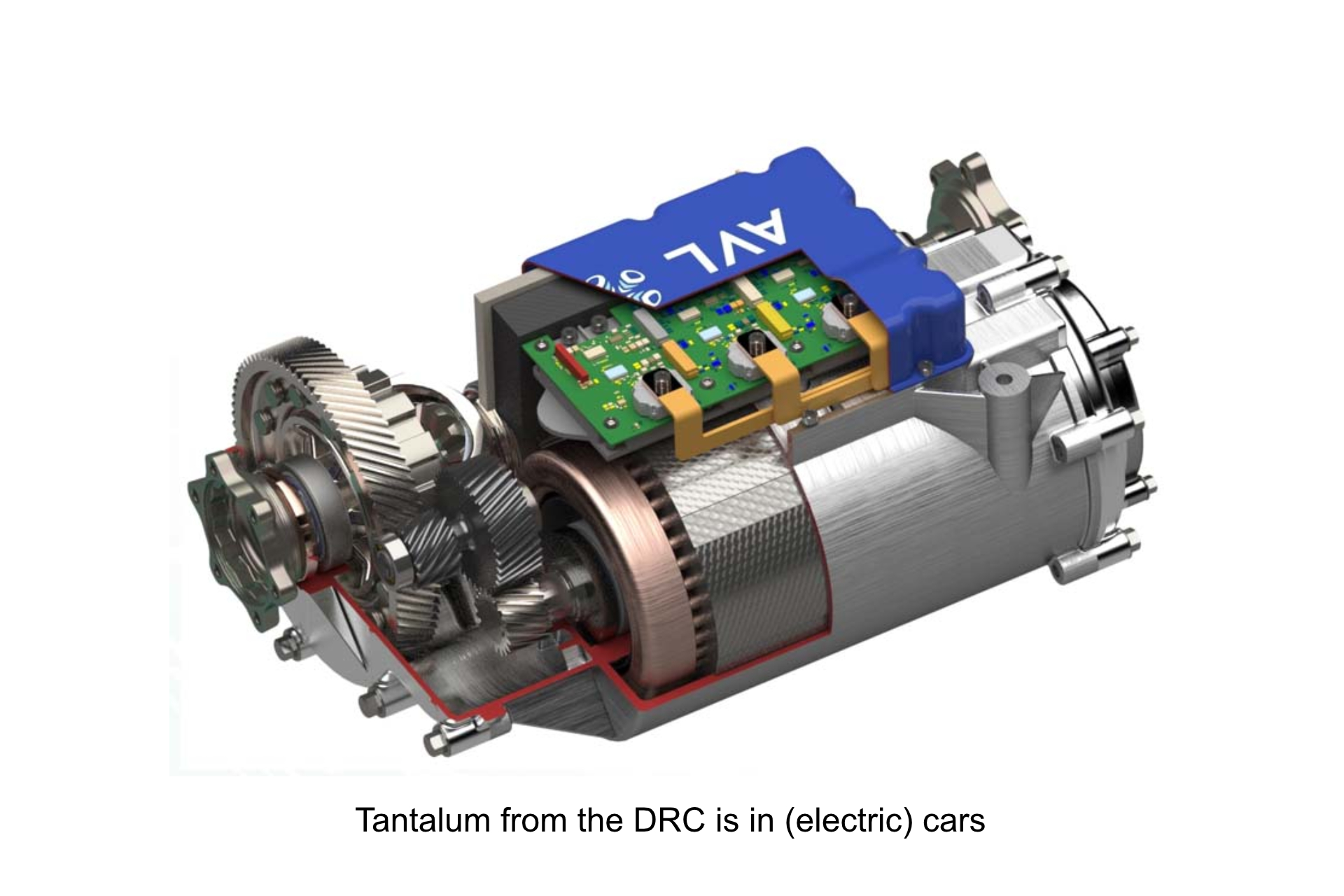
FOR WHAT ARE THEY FIGHTING? What is coltan used for?
What is cobalt used for? Cobalt is a chemical element; it has the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, somewhat brittle, gray metal. Cobalt-based blue pigments (cobalt blue) have been used since antiquity for jewelry and paints, and to impart a distinctive blue tint to glass. The color was long thought to be due to the metal bismuth. Miners had long used the name kobold ore (German for goblin ore) for some of the blue pigment-producing minerals. They were so named because they were poor in known metals and gave off poisonous arsenic-containing fumes when smelted
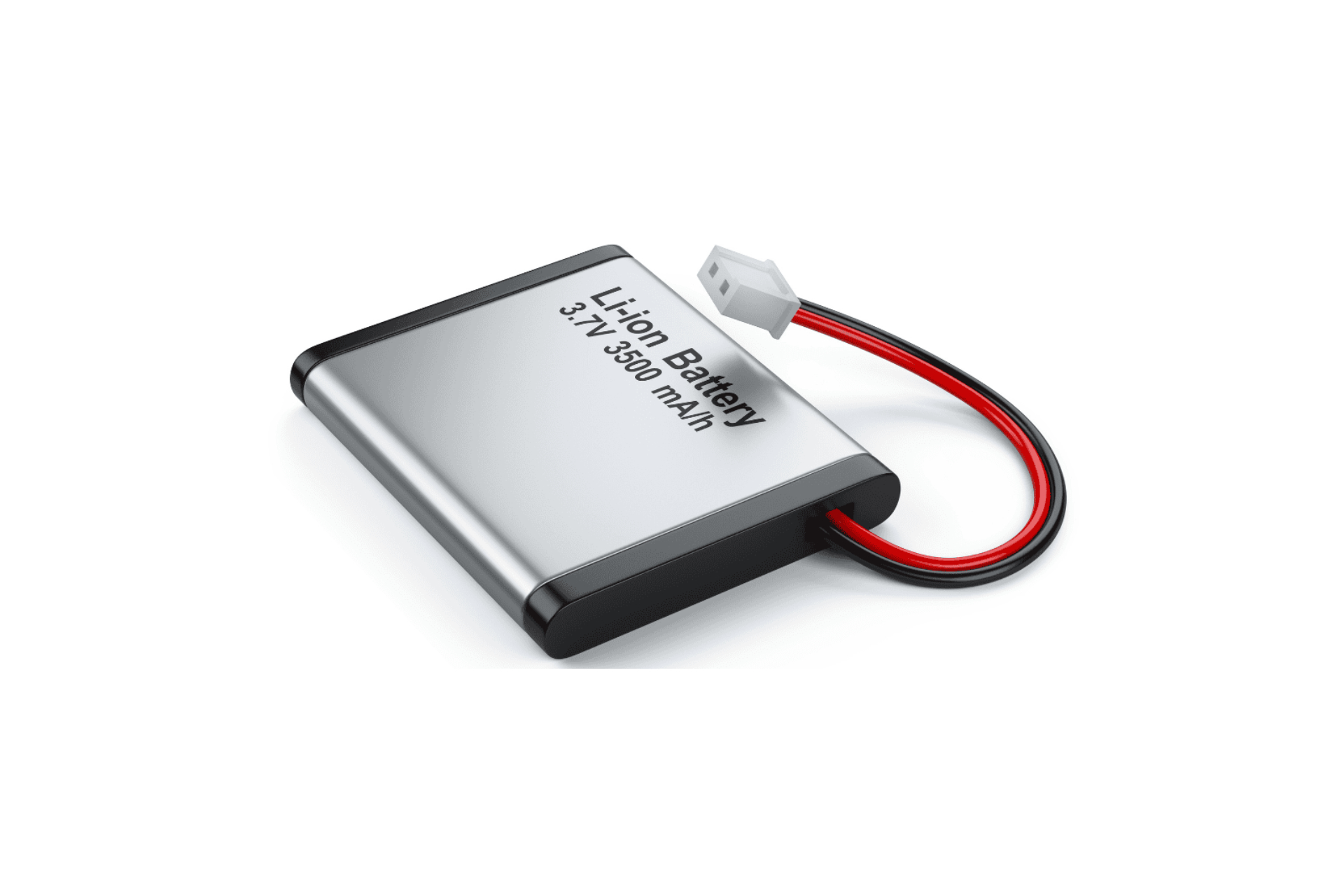
Cobalt is primarily used in lithium-ion batteries. |
|
IN WHOM INTEREST IS THIS WAR? Rwanda I don't look at political aspects but material aspects. Here are a few examples in reports from the United Nations Security Council indicating Rwanda's interest in minerals from North Kivu.
China
Consumers As consumers, we all are part of the conflict because our homes are filled with tantalum, and carry it in our mobile phones, and smartwatches. Some people even have tantalum in their jewelry. It is not in our collective buying behavior to be critical and it is also not what manufacturers want to see. Producing, selling and making money is what it is all about, not human lives. Hence the indifference among buyers and sellers. The unchanged collective behavior among consumers naturally raises the question "Is a change in this behavior possible?" A change is always possible if there is a will and that has not been the case for years because of advertising campaigns to keep everyone buying. It is about a vicious circle of supply and demand. |
|
THE KEY PLAYERS
In the 1980s, Kagame fought in Yoweri Museveni's rebel army becoming a senior Ugandan army officer after many military victories led Museveni to the Ugandan presidency. Kagame joined the RPF, taking control of the rebel group when the previous leader Fred Rwigyema died on the second day of the 1990 invasion By 1993, the RPF controlled significant territory in Rwanda and a ceasefire was negotiated. The assassination of Rwandan President Juvénal Habyarimana set off the genocide, in which Hutu extremists killed an estimated 500,000 to 800,000 Tutsi and moderate Hutu. Kagame resumed the civil war and ended the genocide with a military victory. The genocide is the worst example of tribalism in politics in black Africa's history. Rwanda has only known four presidents. Paul Kagame made an end to fair elections 25 years ago, on April 22, 2000. Since 2003, he has been "re-elected" time and time again as elections are manipulated in various ways. Manipulations include banning opposition parties, arresting or assassinating critics, and electoral fraud. According to its constitution, Rwanda is a multi-party democracy with a presidential system. In practice, it functions as a one-party state ruled by the Rwandan Patriotic Front and its leader Paul Kagame.
Like the Rwandan constitution, the Ugandan constitution doesn't reflect reality. In the Political Parties And Organizations Act 2005, it is to read: " Every citizen of Uganda has a right to form or join a political party or organization of his or her choice." and "The people shall express their will and consent on who shall govern them and how they should be governed, through regular, free and fair elections ..." Well, the case of Bobby Wine has proven that even Uganda is defacto a one-party state.
On January 1, 2025 and during an interview with Al Jazeera, Bisimwa claimed that he was fighting a "defensive" war. The Qatari broadcast was punished for the interview and banned from reporting in the DR Congo for nine months. However, a background check learns that Bisimwa is since April 2012 the head of the militia group while the Rwandan ruler, Paul Kagame is destablizing the North Kivu province since 2004 over minerals. It is in 2012 that the M23 first saw action during its first rebellion against the Congolese government that led to the displacement of large numbers of people. A United Nations report found that Rwanda (read: Kagame) created and commanded the M23 rebel group. Rwanda ceased its support due to international pressure and the military defeat by the Congolese military and the UN peacekeeping forces in 2013. So, how do I view the relationship between the two countries? There is a tradition in black Africa. If you (read: Kagame) have something in your life that connects you with people in any of the black African countries, you will be seen as one of them. |






 The country is considered one of the 17 megadiverse nations and is one of the most flora-rich countries on the African continent.
The country is considered one of the 17 megadiverse nations and is one of the most flora-rich countries on the African continent.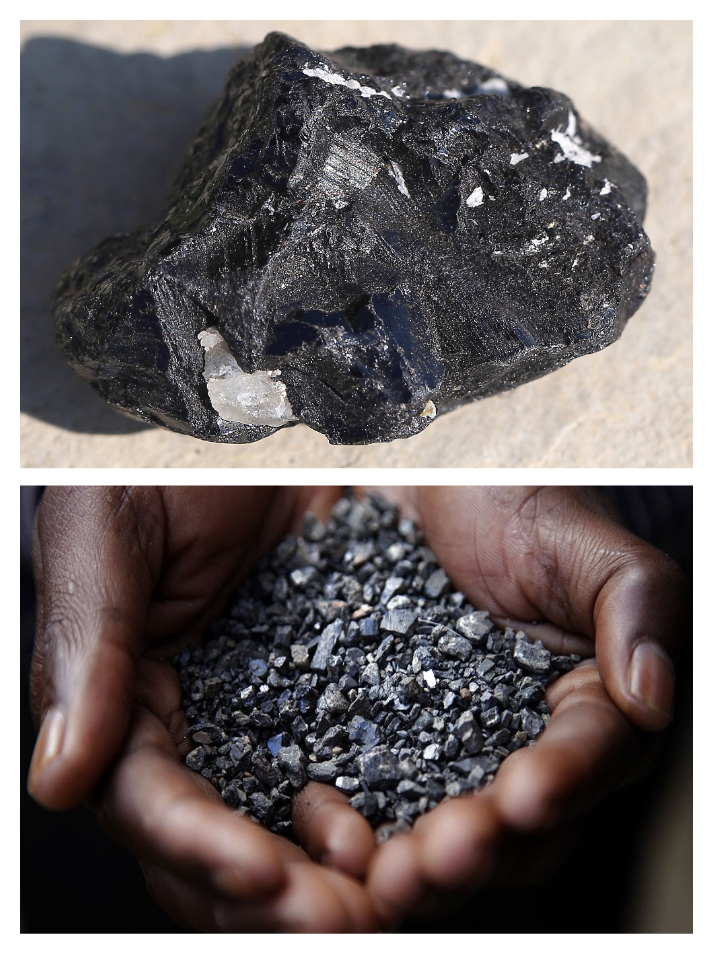 The Democratic Republic of Congo is considered the world's richest country in terms of wealth in natural resources. Most of the raw mineral deposits remain untapped and are worth an estimated $24 trillion. These deposits include the world's largest coltan reserves and considerable amounts of cobalt.
The Democratic Republic of Congo is considered the world's richest country in terms of wealth in natural resources. Most of the raw mineral deposits remain untapped and are worth an estimated $24 trillion. These deposits include the world's largest coltan reserves and considerable amounts of cobalt. 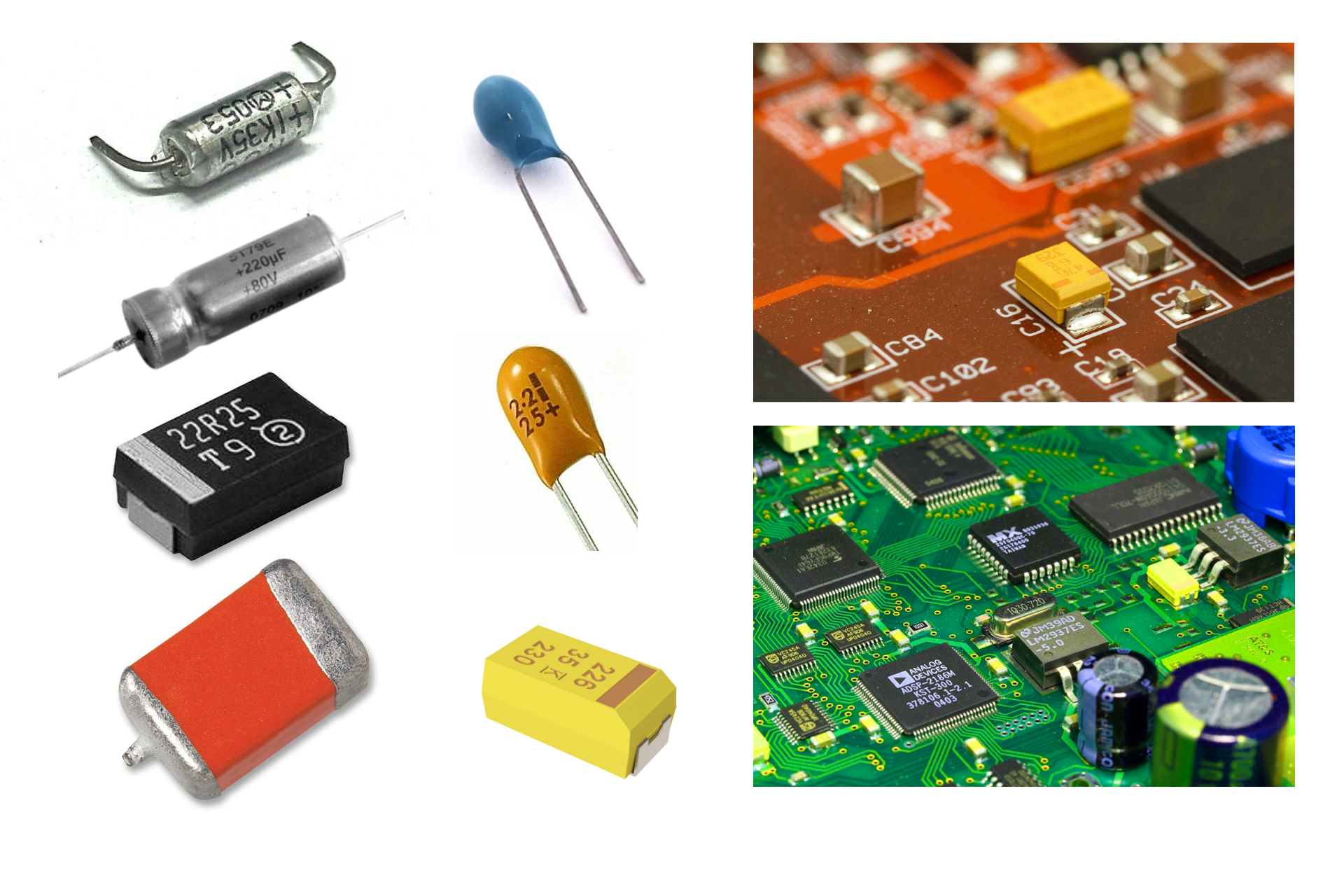 Coltan (short for columbite–tantalites and known industrially as tantalite) is a dull black metallic ore from which the elements niobium and tantalum are extracted. The niobium-dominant mineral in coltan is columbite (after niobium's original American name columbium), and the tantalum-dominant mineral is tantalite.
Coltan (short for columbite–tantalites and known industrially as tantalite) is a dull black metallic ore from which the elements niobium and tantalum are extracted. The niobium-dominant mineral in coltan is columbite (after niobium's original American name columbium), and the tantalum-dominant mineral is tantalite.
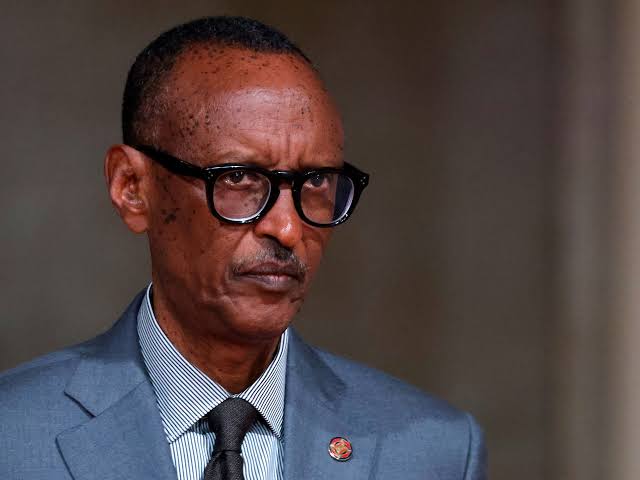








 Paul Kagame was born into a Tutsi family in southern Rwanda that fled to Uganda when he was two years old. He spent the rest of his childhood there during the Rwandan Revolution, which ended Tutsi political dominance.
Paul Kagame was born into a Tutsi family in southern Rwanda that fled to Uganda when he was two years old. He spent the rest of his childhood there during the Rwandan Revolution, which ended Tutsi political dominance. Like Kagame, Yorowi Museveni, Uganda's long sit-tight dictator has a militant background as he was a Front for National Salvation member. In Uganda, nine people who have ruled the country were military officers. In 1981, Yoweri Museveni carried out a coup against the then-dictatorship of Milton Obote. The first elections under Museveni's government were held on May 9, 1996. He was sworn in as president for the second time on May 12, 1996, and remained in power since then. In 2004, the government proposed to amend the Constitution to enable Museveni to rule for life.
Like Kagame, Yorowi Museveni, Uganda's long sit-tight dictator has a militant background as he was a Front for National Salvation member. In Uganda, nine people who have ruled the country were military officers. In 1981, Yoweri Museveni carried out a coup against the then-dictatorship of Milton Obote. The first elections under Museveni's government were held on May 9, 1996. He was sworn in as president for the second time on May 12, 1996, and remained in power since then. In 2004, the government proposed to amend the Constitution to enable Museveni to rule for life.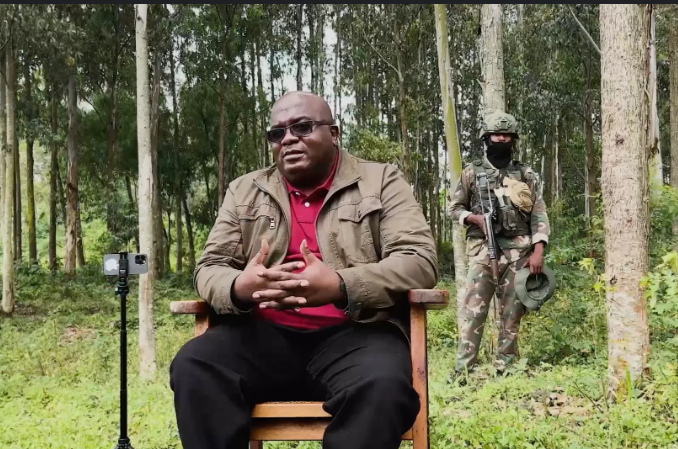 Bertrand Bisimwa is the 'president' of the rebel group 'March 23' (M23), and Emmanuel Sultan Makenga the military chief. Bisimwa stood alongside Nangaa at the launch of AFC and is central to AFC and M23's collaboration.
Bertrand Bisimwa is the 'president' of the rebel group 'March 23' (M23), and Emmanuel Sultan Makenga the military chief. Bisimwa stood alongside Nangaa at the launch of AFC and is central to AFC and M23's collaboration.






